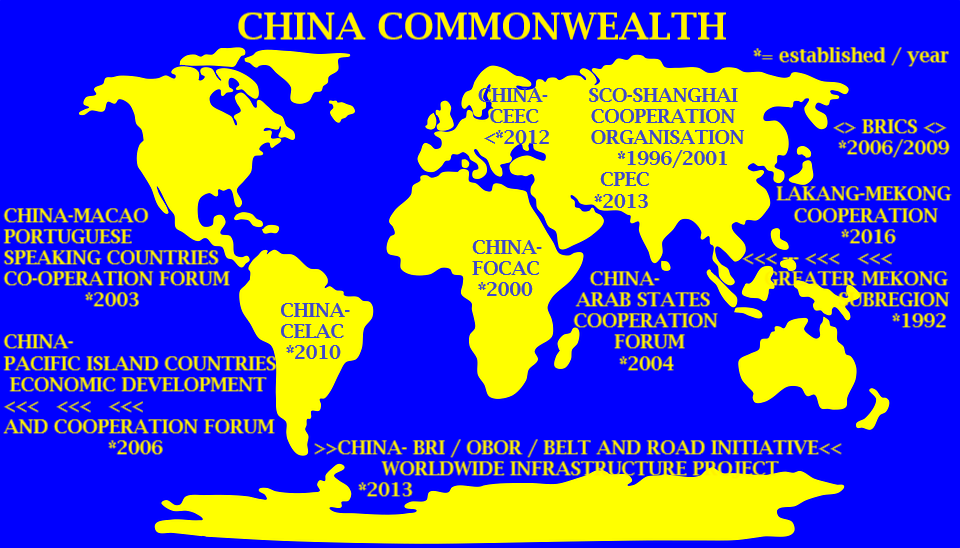
In der Graphik (siehe Titelfoto) und hier gelistet, sehen sie jene Organisationen, die China installierte, um ökonomisch weltweit Fuß zu fassen.
In Euro- Medien werden sie darüber kaum Berichterstattung finden, weil es das Image der USA – die ja noch immer als Wirtschaftsmacht Nummer 1 dargestellt wird (es aber schon lange nicht mehr ist) – weil also das US- Image nicht „angekratzt“ werden soll.
China- Belt and Road Initiative / established 2013
Worldwide Infrastructure Projects
The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) was unveiled in 2013 by China’s president Xi Jinping and since then has been ubiquitous around the world.
https://www.oboreurope.com/en/
https://www.mfa.gov.cn/ce/cegv/eng/zywjyjh/t1675564.htm
###################################
China-Arab States Cooperation Forum / established 2004
The China-Arab States Cooperation Forum is a formal dialogue initiative between China and the Arab League.
http://www.chinaarabcf.org/ara/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/China%E2%80%93Arab_States_Cooperation_Forum
###################################
Die größte und mächtigste Organisation weltweit: Die SCO – sic!
SCO – Shanghai Cooperation Organisation / established 1996 / 2001
The Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO), also known as the Shanghai Pact, is an Eurasian political, economic, and security alliance. It is the world’s largest regional organisation in geographic scope and population, covering three-fifths of the Eurasian continent, 40% of the world population, and more than 20% of global GDP.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shanghai_Cooperation_Organisation
###################################
BRICS *2006/2009
BRICS is the acronym coined to associate five major emerging economies: Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa. The BRICS members are known for their significant influence on regional affairs.[1] Since 2009, the governments of the BRICS states have met annually at formal summits. India hosted the most recent 13th BRICS summit on 9 September 2021 virtually.
https://bricspolicycenter.org/en/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/BRICS
###################################
China- CELAC / established 2010
We, the Foreign Ministers and representatives of the People’s Republic of China and the member countries of the Community of Latin American and Caribbean States (CELAC), held the First Ministerial Meeting of the China-CELAC Forum (CCF) under the theme of „New Platform, New Starting Point, New Opportunity – Joint Efforts to Promote China – Latin America and the Caribbean Partnership of Comprehensive Cooperation“ on January 8th and 9th, 2015 in Beijing.
http://www.chinacelacforum.org/eng/zywj_3/201501/t20150123_6475938.htm
http://www.chinacelacforum.org/eng/
###################################
China- CEEC (17+1) – Cooperation between China and Central and Eastern European Countries / established 2012
Cooperation between China and Central and Eastern European Countries (China-CEE, China-CEEC, also 16+1; during 2019-2021 – 17+1) is an initiative by the Chinese Ministry of Foreign Affairs to promote business and investment relations between China, officially known as the People’s Republic of China (PRC) and 16 countries of Central and Eastern Europe (CEE, CEEC): Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Czechia, Estonia, Greece, Hungary, Latvia, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Poland, Romania, Serbia, Slovakia and Sloveniahttp://www.china-ceec.org/eng/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cooperation_between_China_and_Central_and_Eastern_European_Countries
###################################
Greater Mekong Subregion / established 1992
The Greater Mekong Subregion, (GMS) or just Greater Mekong, is a transnational region of the Mekong River basin in Southeast Asia. The region is home to more than 300 million people. It came into being with the launch of a development program in 1992 by the Asian Development Bank that brought together the six Asian countries of Cambodia, China (specifically Yunnan Province and the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region), Laos, Myanmar (Burma), Thailand, and Vietnam.
https://www.greatermekong.org/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Greater_Mekong_Subregion
###################################
Lakang-Mekong Cooperation / established 2016
The Lancang-Mekong area is one of the regions with the greatest development potential in Asia and beyond. Lancang and Mekong differ in name, but refer to the same river—an important river running across China and the Indo-China Peninsula. Originating from China’s Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, the river has its source in Yushu of Qinghai Province. It is called Lancang River in China, while in its downstream after flowing out of Yunnan Province, it is called the Mekong River, running across Myanmar, Laos, Thailand, Cambodia, and Vietnam, measuring 4,880 kilometers in length, covering an area of 795,000 square kilometers, and feeding altogether 326 million people.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lancang-Mekong_Cooperation
###################################
China–Pacific Island Countries Economic Development and Cooperation Forum/ established 2006
Hu kündigte die weitere Unterstützung der Pazifik-Insel-Staaten durch China an, sowie die wirtschaftliche und soziale Entwicklung des 8-Initiativen- Plans.
###################################
China- Macao / established 2003
Forum for Economic and Trade Co-operation between China and Protuguese-speaking Countries
The Forum for Economic and Trade Cooperation between China and Portuguese-speaking Countries (Macao), also known as Forum Macao, was launched in October 2003. It resulted from an initiative by China’s Central Government, in co-ordination with seven Portuguese-speaking Countries — namely Angola, Brazil, Cape Verde, Guinea-Bissau, Mozambique, Portugal and East Timor — and with the collaboration of the Government of the Macao Special Administrative Region (Macao SAR). São Tomé and Príncipe joined Forum Macao in March 2017, becoming the eighth Portuguese-speaking Country to join the organisation.
https://www.forumchinaplp.org.mo/
###################################
CHINA- FOCAC / established 2000
As prescribed in the Program for China-Africa Cooperation in Economic and Social Development, adopted at the 2000 Ministerial Conference of FOCAC, China and Africa agreed to set up joint follow-up mechanisms to conduct regular evaluations on the implementation of the follow-up actions. In July 2001, a FOCAC ministerial consultation meeting was held in Lusaka, capital of Zambia, at which the Procedures for Follow-up Mechanisms of FOCAC were deliberated and adopted. The follow-up mechanisms officially took effect in April 2002. The FOCAC follow-up mechanisms are built at three levels: The Ministerial Conference is held every three years; the Senior Officials Follow-up Meeting and the Senior Officials Preparatory Meeting for the Ministerial Conference are held respectively in the year and a few days before the Ministerial Conference is held; and the consultations between the African Diplomatic Corps in China and the Secretariat of the Chinese Follow-up Committee are held at least twice a year.
http://www.focac.org/eng/
###################################
China–Pakistan Economic Corridor / established 2013
China–Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) (Chinese: 中巴经济走廊; pinyin: Zhōng bā jīngjì zǒuláng; Urdu: چین پاکستان اقتصادی راہداری) is a collection of infrastructure projects that are under construction through out Pakistan beginning in 2013. Originally valued at $47 billion, the value of CPEC projects is worth $62 billion as of 2020. CPEC is intended to rapidly upgrade Pakistan’s required infrastructure and strengthen its economy by the construction of modern transportation networks, numerous energy projects, and special economic zones. On 13 November 2016, CPEC became partly operational when Chinese cargo was transported overland to Gwadar Port for onward maritime shipment to Africa and West Asia,[10] while some major power projects were commissioned by late 2017. All the progress for CPEC after COVID-19 pandemic alert in Pakistan as of 2021 has been haulted due to security concerns of the workers and the protests being carried out in the Northwest-Frontier Province and Balochistan.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/China%E2%80%93Pakistan_Economic_Corridor
###################################